Excretory system
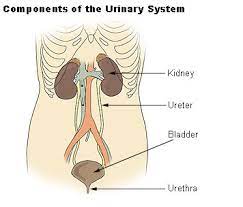
It is also called the urinary system
It includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters and the urethra
The urinary system is nearly identical in most mammals, mainly differing in amount of water reabsorption
Ammonia is a toxic byproduct of breakdown of food
Mammals,amphibians,and some marine animals convert ammonia into urea
Other animals which don't have a lot of water like birds turn ammonia into uric acid which comes out like a paste
The regulation of amount of water and dissolved substances in the body is called osmoregulation
Kidney:
Kidneys maintain water and dissolved substance level & maintain blood pressure
Kidneys filter fluid and dissolved substances out of the blood and reabsorb 99% of them back into the blood, the rest is excreted as urine
The are two main layers of the kidney are called:
The renal cortexThe word cortex means tree bark and is used to indicate the outer layer of a thing which contains the glomerulus, bowman's capsule and the proximal and distal convoluted tubules
The renal medullaMedulla means the pith and used to indicate the inner layer which is the center of the kidney the medulla gets slatier the closer it is to the center
The main artery is the renal artery and the man vein is the renal vein, there are also other arteries and veins prominently the vasa recta
Nephrons:
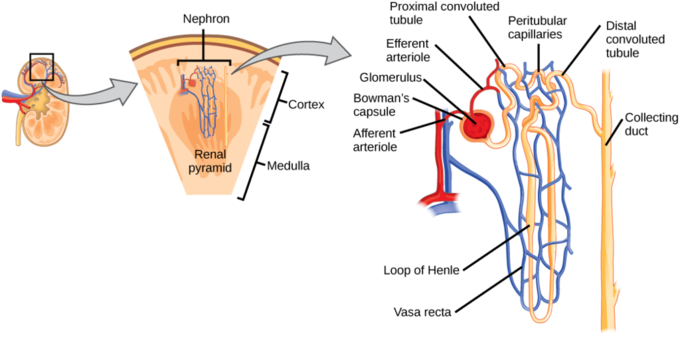
Each kidney is the size of a mango and contains millions of nephrons
Nephrons are tiny filtering structures
Working of nephrons:
Glomerulus:
Blood from the heart enters the kidneys from the renal arteries into many capillaries until it enters tangled up porous capillaries called the glomerulus
The glomerulus is the starting point of the nephron
Bowman's capsule:
The glomerulus has very high pressure and squeezes out around 20% of the fluid from the blood into a cup like sac called the Bowman's capsule
The fluid and dissolved substances squeezed out are called the filtrate and consists of water, urea and small ions and molecules
Proximal convoluted tubule:Translates into the "very twisty tube near the beginning"
From the bowman's capsule, the filtrate flows into a twisted tube called the proximal convoluted tubule
Osmoregulation takes place here and in the other tubules with specialised pumps and other types of active and passive transport
In here, mainly organic solutes like glucose, amino acids are reabsorbed but some sodium, potassium and water is also reabsorbed
Loop of Henle:
From the proximate convoluted tubule, the filtrate enters the loop of Henle
The loop of Henle is a long and hair pin shaped tubule passing through both main layers of the kidney
Most of the reabsorption happens in the loop of Henle
The loop of Henle absorbs most of the water on descending end, as the membrane is permeable to water and the medulla is hypertonic
It pumps out the salts we need on ascending end, here the membrane is not permeable to water, it's line with ion channels.
As the filtrate ascends it enters the less salty layers of the medulla and salt flows out from the filtrate to the medulla
By pumping out the salt it makes the medulla hypertonicVery salty compared to the filtratecreating a concentration gradient that makes the medulla absorb more water from the other nephrons
Distal convoluted tubule:Farther away curly tube
As the filtrate exits the ascending end of the loop of Henle, it enters the distal convoluted tubule
The distal tubule regulates the amount of potassium,sodium and calcium with the help of pumps and hormones regulating the reabsorption process
Collecting ducts:
As the filtrate exits the distal convoluted tubule, it is mainly water,urea and other metabolic wastes and turns into urine as it enters the collecting ducts
The collecting ducts channel the urine to the medulla which absorbs water as it is hypertonic
There are hormones that tell the collecting ducts how porous to make their membrane, this regulates how much water gets reabsorbed from the urine
Anti diuretic hormone reduces the amount of water in urine
Alcohol interferes with the anti-diuretic hormone, this makes you pee more water
Ureters:
After being filtered by the kidneys, the urine goes through tubes called ureters into the bladder
Urinary bladder:
Urine gets into the bladder and is stored there until the animal urinates
Urethra:
When the animal pees the urine exits the bladder through a sphincter into a tube called the urethra from which it exits the body
The urethra is longer in men reducing their risk of an UTI




